It’s not even a question, ranking higher than your competitors on Google is a must. Let’s face it, having your name above your competition’s name is always nice. But whether you’re just getting started with a new website or improving your existing site, this shows useful, tactical suggestions for powering up your SEO game.
In 2011, Search Engine Watch reported that a research study by Optify discovered that “websites ranked number one received an average click-through rate (CTR) of 36.4 percent; number two had a CTR of 12.5 percent, and number three had a CTR of 9.5 percent.”
In fact, SEO’s organic results are being clicked 94% of the time compared to paid search. And, as you’re obtaining more traffic, you’re gaining more potential sales without having to pay for a costly ad.
The problem is this: SEO is simple in theory but complicated and competitive in practice. Google alone reported using hundreds of different factors to analyze its search ranking. So, what can you do to influence your ranking? Are there basic SEO principles to follow?
Keyword Research & Placement
Identify the keywords that shoppers use when they are searching for a particular product. For example, you want your online shoe store to display when shoppers type “shoes” or when they search for “buy running shoes.”
Head keywords are singular terms that are broad and far-reaching while combining multiple terms called “long-tail keywords” are highly specific. While it’s tempting to use singular keywords as they often have high search volume, they are considered to be highly competitive.
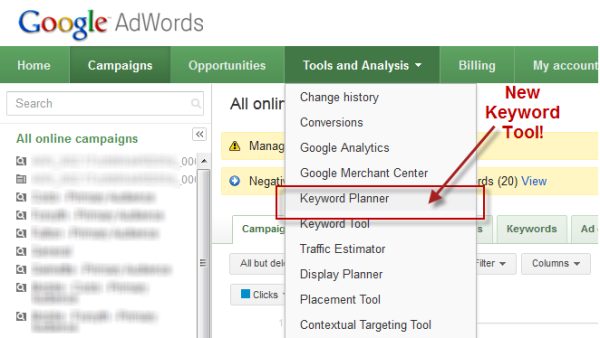
Use keyword search tools such, like the WooRank keyword tool to help you identify which keywords are relevant to your online store. For example, if you’re a jacket retailer for women, avoid using the broad term “jackets”. Instead, use this head keyword to look for alternative long-tail keywords.
Once you have your list of keywords, the next step is to put them to use. The basic implementation is through your website’s elements. Below are the good places to optimize:
- Titles
- Descriptions
- Headings & Content
- Images Titles & Alt Text
- URLs
Create Distinct and Relevant Content
Google is an advocate of “Make pages primarily for users, not for search engines“.
Their goal is to provide users with only relevant information. This is why adding value by creating and distributing contents that are unique and relevant to your target audience is critical in SEO.
Begin by including a blog on your website that tackles topics related to your brand/ products. Understand what your target market is interested to see or address a question they want to know.
Optimize Each Product Page with Focus Keywords
Majority of an eCommerce site’s pages are devoted to products. Thus, optimizing individual product pages is also vital to your SEO strategy. If you don’t have any SEO in place for each of your product pages, then how can potential shoppers find about your products?
Focus on keywords that would best describe your products. As you’ve learned about keyword research earlier, try to find out terms that most shoppers use when looking for similar products. Once you’ve identified the focus keywords for a product, you need to include them in your product page elements such as header tags, alt tags, meta title, meta description, and product description.
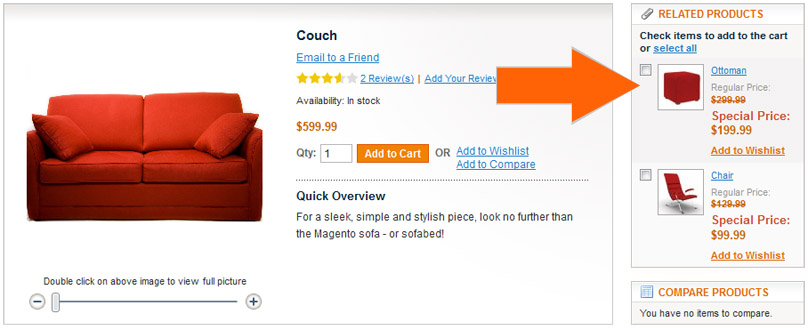
Display Related Products
Even Google uses related search suggestions to help its users find what they’re searching for more quickly. You can even see “People also ask for” suggestions when you search for answers. This signals that Google is an advocate of enhancing the user experience by simply helping out the users.
Apply this logic by displaying related products to the current item being viewed by the user. By doing so, you’re creating quality contents because of the useful information that your visitors might be interested in. Again, unique and useful contents impact your SEO strategy.
Optimize for Image Search
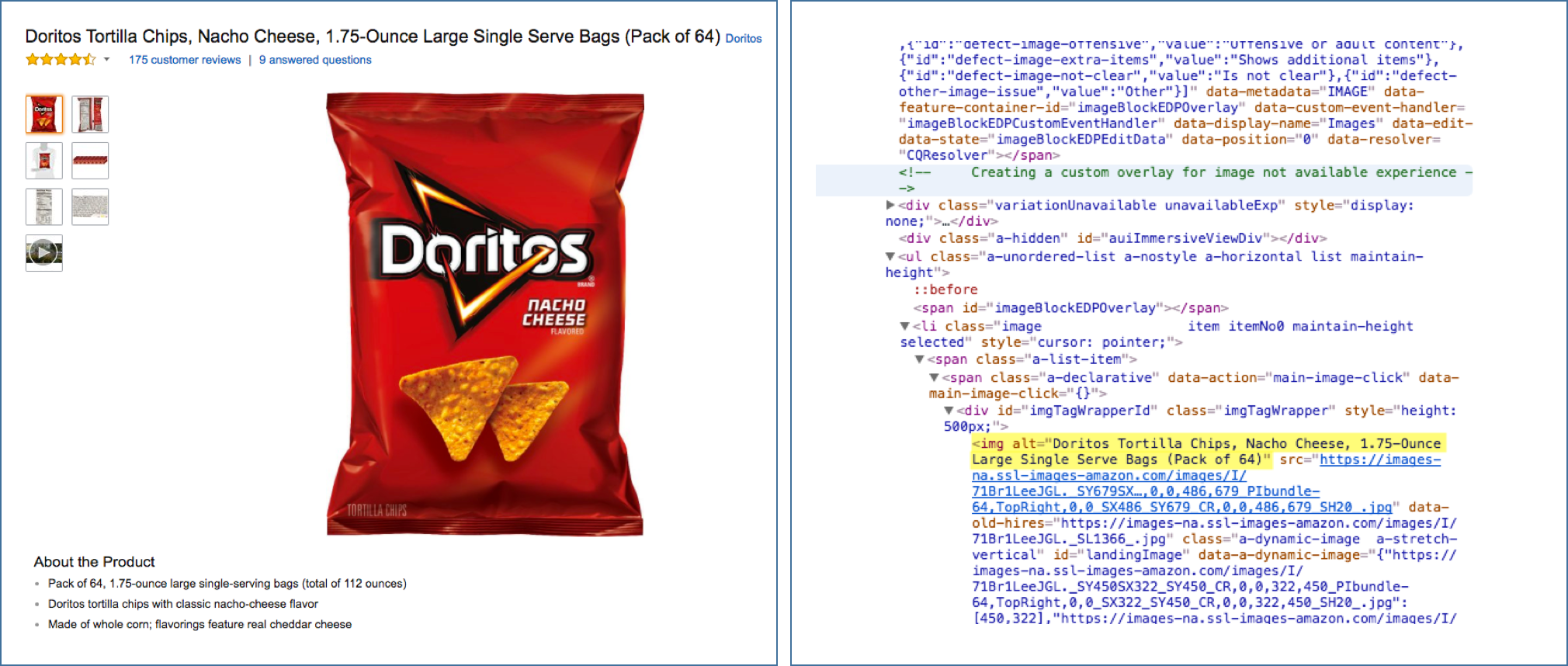
Searching for products using the “Image” function has been widely popular as well. The idea is shoppers can visually see the products that interest them and then just click the image to direct them to the online store. So, it’s important to optimize your product image for search too.
Add focus keywords to your image by using ALT tags. The term “ALT tag” is commonly used to refer to the texts that describe a picture in a web content. Using descriptive ALT tags can affect your products to show up in the Image Search. They are also essential accessibility element for those visually impaired individuals.
Optimize Anchor Texts
When you use internal links to your site for visitor navigation, you typically use the word “click here” to do so. The words used in the link are called “anchor texts”. You can optimize them for SEO purposes by substituting the typical “click here” with keywords that are relevant.
Use descriptive anchor texts to enhance your user experience. For example, instead of writing “Click here to visit Beeketing, best eCommerce software service provider”, anchor your link to “Visit Beeketing, best eCommerce software service provider.”
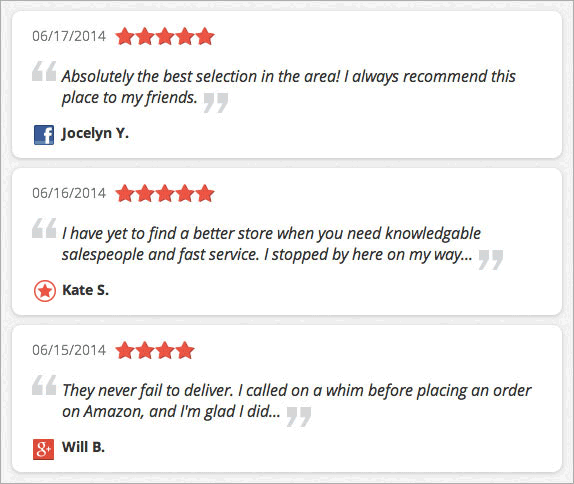
Heighten Positive Customer Reviews
Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines include customer reviews as one source for assessing the reputation of a webpage. Allocate a space in your site or product page where your customers can leave reviews. Not only that you’re increasing your contents on your site, but you’re also providing potential visitors with information that could help in their purchase decision.
Amplify positive customer reviews, not negative ones as Google uses the lowest quality rating for websites with extremely negative reviews. Incentivize your shoppers to leave a positive feedback about their experience or regarding the product they bought.
Quality Link Building
A common misconception is the more inbound and outbound links a site has, the better the ranking it will get. However, the real case is quality trumps quantity. What matters in SEO is quality link building as this affects credibility and traffic.
The sites that you link to and receive links from must bear good reputation and traffic. If, for instance, you linked to low-quality sites or those blacklisted by Google, then it’s likely that you’ll get penalized for the backlinks causing lower SERP ranking.